Lubawa- Warmian-Masurian 作者: 来源: 发布时间:2021-10-27
Ⅰ. Population and Area
Population (2017)
• Total 10,269
• Density 610/km2 (1,600/sq mi)
Area
• Total 16.84 km2 (6.50 sq mi)
Website http://www.lubawa.pl

Ⅱ.Natural Geography (environment and resources)
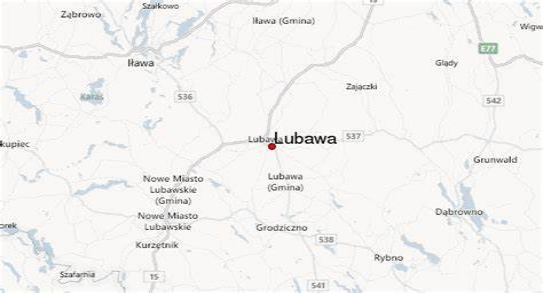
-Lubawa is located in Chełmno Land, approximately 15 kilometres (9 miles) north-east of the town of Nowe Miasto Lubawskie, 55 kilometres (34 miles) south-west of the town of Olsztyn and 115 km (71 miles) south-east of the regional centre of Gdańsk, at an altitude of 145 metres (476 feet) above sea level.
-Transport
-The following roads run through Lubawa:
-15 Trzebnica - Września - Gniezno - Inowrocław - Toruń - Ostróda
-537 - Lubawa - Pawłowo to S7
-541 - Lubawa - Lidzbark - Żuromin - Sierpc - Dobrzyń on the Vistula
-There is a freight train station in the town.
Ⅲ.Economy
-The city is the seat of the company Lubawa, listed since 1996 on the Stock Exchange .
-Companies located in the industrial district of Borek play an important role in the economic development, such as IKEA Industry (the largest factory in the region and one of the largest and most modern in Poland [ note needed ] producing furniture for the Swedish company IKEA ), Szkłomal (dealing with the production of mirrors and furniture made of glass) or the carpentry company Szynaka Meble.
-http://www.lubawa.pl/
Ⅳ.Industrial Characteristics
-Lubawa is an important centre of furniture industry. Also, a "Lubawa S.A." company is located there, which is the biggest Polish producer of military equipment such as bulletproof vests, currently used by the Polish Army and the Polish press.
-https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lubawa#Economy
-Key projects
-1. Me on the Internet" project
-http://lubawa.bip-wm.pl/public/
-2. Benefit 300 "GOOD START"
-300 zlotys - this is the amount of the "Dobry Start" benefit for each learning child. The government has established a program under which families will receive PLN 300 once a year for each child attending school - regardless of their income. For the first time, the benefit will go to families this year.
-Who is the support for?
-The "Dobry Start" benefit is granted once a year for children up to the age of 20 who begin the school year.
-Children with disabilities studying at school will receive them until they turn 24.
-The family will be able to count on support regardless of their income.
-http://lubawa.bip-wm.pl/public/?id=167535
Ⅴ.Attrations

Remains of the Lubawa Castle
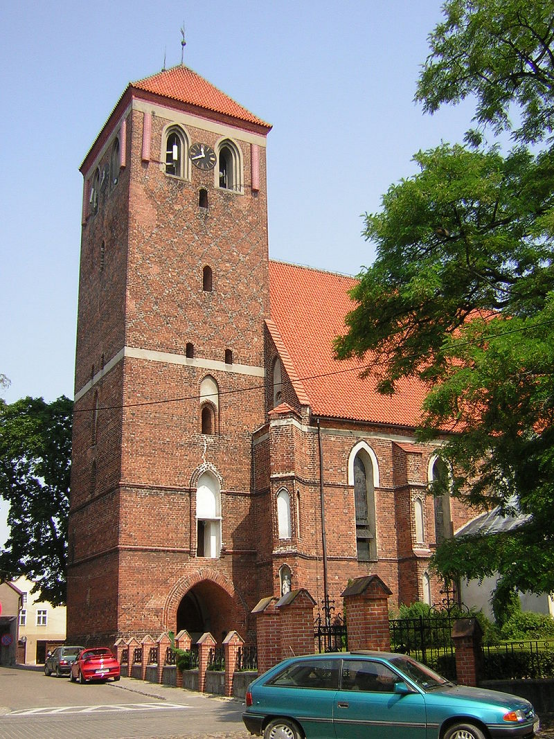

Gothic church St. Anna in Lubawa (1330).
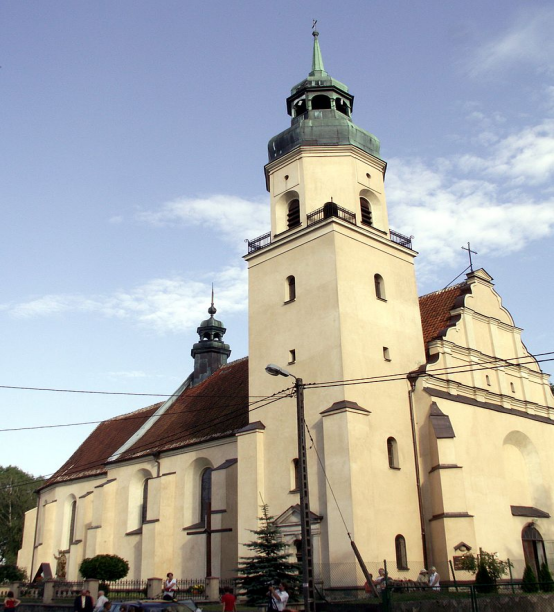

Selected historic churches, from the left: St. John the Baptist, St. Barbara, Visitation church
-According to the register of monuments of the National Heritage Institute, the following objects are entered on the list of monuments in Lubawa :
-Religious buildings
-Parish Church of st. Anna, tz. Parish church - from 1330 with the Mortęski chapel from 1581. Rich interior furnishings. Sanctuary of Our Lady of Leipzig. At the parish of the Lubawa Region Museum, registry number: 265 (L / 51) from March 20, 1957
-Parish Church of st. John the Baptist and St. Michael the Archangel, so. Jan - built 1603-1608, the parish was erected in 2000 from the parent part of the parish of the Visitation of the Blessed Virgin Mary and St. Anna in Lubawa, the most beautiful monuments of the temple include the coffered, figural-ornamental ceiling of the nave from 1612, carved and polychrome ceiling of the chancel, mannerist stalls - richly carved and polychrome, a Renaissance pulpit and a 14th-century crucifix with which the Saxon Franciscans came to visit. Reg.No .: 264 (L / 50) from March 22, 1957
-Wooden parish church. pw. st. Barbara , tz. Barbarka - 1673, reg.no .: 89 from 28/09/1953
-Bernardine monastery complex - XIV, XVII-XVIII, former primary school, register number: 409 (L / 49) from 4.08.1957
-pilgrimage chapel of the Visitation of the Blessed Virgin Mary in Lipy - 1870
-Secular objects
-Remains of defensive walls, ul. Pod Murami, Pomorska, Bankowa - after 1300, XIV-XVI, registration number: 243 (L / 88) from 1 August 1957 and 1145 from 2 May 1968
-ruins of the castle of the Chełmno bishops - XIV, registry number: 408 (L / 11) from August 4, 1957
-Team of the city hospital st. George from the second half. XIX century, reg.No .: A-2502 of 8.09. 2003:
-Hospital, ul. Grunwaldzka 11a
-Chapel, 13 Grunwaldzka St.
-Convent of the Sisters of Mercy, ul. st. Barbara 2, 4, 6
-fence
-Municipal Public Library Teofil Ruczyński
Ⅵ.History and Culture
-The origins of the city
-The first reference to the land of Lubawa, mentioning the existence of a castle in Lubawa, comes from 1216. This is evidenced by the document signed by Pope Innocent III of January 18 of the same year, in which he confirmed to Christian - the Prussian bishop - the possession of the Lubawa land as a donation from the newly converted ruler Prussian Surwabuno . From 1257, Lubawa and its vicinity became the property of the Chełmno bishopsand became the administrative center of a significant complex of episcopal estates known as the Lubawa key. The bishops built a magnificent castle in Lubawa, which was their residence. In 1260, the town was already a significant urban and defensive center. In 1269, Lubawa was destroyed during the invasions of the Prussians from the Sudov tribe. Thanks to the efforts of the inhabitants, it was rebuilt quite quickly. Appreciating this effort, the Chełmno bishop Herman (1303-1311) issued a location privilege for Lubawa. Unfortunately, this document has not survived to our times. Only the renewed location privilege for Lubawa, this time the bishop of Chełmno Otto from April 13, 1326, mentions this. After 1326, Lubawa developed on the basis of the principles of Chełmno lawgradually creating a local government body, i.e. the city council. In 1330, the city was invaded by Lithuanian troops led by Gedymin. In 1422 Grand Master Paul von Rusdorf gathered a large army near Lubawa, wanting to start a battle, having found out about the size of Władysław Jagiełło's army, he ordered a retreat, and many of his knights were then taken prisoner.
-First Rzeczpospolita
-In 1440, the city joined the Prussian Union fighting against the Teutonic Order, in 1454 the Union's troops occupy the castle, and King Kazimierz IV Jagiellon, at the request of the Union, announces the inclusion of the region into the Polish Crown . In 1459 the city was invaded by the Teutonic Knights and they kept it until 1464, when the city was returned to Polish hands. In the Peace of Toruń (1466) it was confirmed that Lubawa and its surroundings belonged to Poland. The city belonged administratively to the Chełmno Province until the first partition of Polandin 1772. The town flourished most rapidly in this period. Trade and crafts developed in particular. In 1521, in the outskirts of Lubawa, a battle took place during which the Teutonic Knights were repelled by the Polish castle crew. Nicolaus Copernicus stayed four times in the bishop's castle in the years 1535–1539, the longest in 1539, from June to September. It was then that a decision was made to publish the work De revolutionibus orbium coelestium.
-Lubawa became famous not only for the fact that the famous astronomer stayed there, but also for the Gutenberg Bible, also known as the Pelplin Bible. It was bought for the castle of the Chełmno bishops by bishop Mikołaj Chrapicki. Unfortunately, at the beginning of the 19th century, after the borders of the bishopric had changed, the Bible and the capital of the diocese were moved to Pelplin.
-The period of partitions and uprisings and the Duchy of Warsaw
-After the first partition of Poland in 1772, Lubawa came under Prussian rule. Fires and wars as well as the severing of the city's economic and political ties with Poland resulted in its collapse. In 1774 a Prussian garrison was established in Lubawa. At the same time, the new authorities started a colonization action, bringing German settlers, largely of Evangelical faith, to the Lubawa region. In 1785 the seat of the bishopric was moved to Chełmża . By virtue of the Treaty of Tylża of February 7, 1807, the Lubawa land was incorporated into the Duchy of Warsaw. The destruction caused by the Napoleonic Wars worsened the city's situation. Despite the influx of a large number of German people, the Lubawa land retained its Polish character. Patriotic tendencies grew stronger in the city. In the second half of the 19th century, Lubawa and the then Lubawa poviat became a significant center of the Polish national movement in the Prussian partition. This is where volunteers for the insurgent units in 1863 came from, creating the so-called the Lubawa company. This period also brought renewed economic growth to the Lubawa region. The city served as a service center for agriculture.
-The Second Polish Republic, the war occupation and post-war Poland
-Under the Treaty of Versailles, the Lubawa district returned to reborn Poland. On January 19, 1920, enthusiastically welcomed Polish troops of General Józef Haller's army entered Lubawa . A new period in the history of the city began - the interwar period, in which Lubawa still maintained its character as a service base for agriculture. Lubawa belonged administratively to the Lubawa poviat of the Pomeranian Voivodeship , and was also the seat of the "Lubawa" Customs Guard Station.
-The German occupation brought about increased extermination of the Polish population. A juvenile penal camp was located in Lubawa. In 1945, the city was liberated and burned down by units of the 5th armored army of the Second Belorussian Front of the Red Army. War damage reached about 80% of buildings and structures. However, the buildings of sacred architecture that are the pride of the city have survived. In the times of the People's Republic of Poland, Lubawa Zakłady Konfcji Technicznej, Zakłady Aparatury Elektrotechnicznej, a dairy plant, a concrete plant, fruit and vegetable processing plants, a furniture plant, a sawmill and a mill were established in the city.
-The city was a strong cultural and educational center. The first bard of the Lubawa region was the teacher and poet Teofil Ruczyński. The second, Fr. prof. Janusz Stanisław Pasierb . The third author from Lubawa, the poet, is Tomasz Reich.
Ⅶ.Other Information
-Lubawa is a town in the Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship, Poland. It is located in Iława County on the Sandela River, some 18 km (11 mi) southeast of Iława.
Ⅷ.Contact Information
-Government
-Mayor Maciej Radtke
-TOWN HALL 14-260 Lubawa ul. Rzepnikowskiego 9a
-Tel. 89 645-53-00
-Fax. 89 645-53-00
-e-mail : uwad-miasta@lubawa.pl
-NIP : 744-000-55-54
